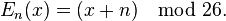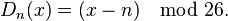Thirty years ago, the first computer virus appeared, Elk Cloner, displaying a short poem when an infected computer booted up for the 50th time. Since then, cybercriminals have created millions of viruses and other malware—email viruses, Trojans, Internet worms, spyware, keystroke loggers—some spreading worldwide and making headlines.
Many people have heard about viruses that fill your computer screen with garbage or delete your files. In the popular imagination, malware still means pranks or sabotage. The early 1990s saw global panic about the Michelangelo virus. In the 2000s, when millions of computers were infected with the SoBig-F virus and primed to download unknown programs from the web at a set time, antivirus companies scrambled to persuade Internet service providers to shut down servers to avoid a doomsday scenario. Hollywood movies like Independence Day reinforced this perception, with virus attacks signaled by flashing screens and alarms.
However, this is far from the truth today.
The threats are no less real now, but they are low-profile, well-targeted, and more likely to be about making cash than creating chaos.
Today, malware is unlikely to delete your hard disk, corrupt your spreadsheet, or display a message. Such cyber-vandalism has given way to more lucrative exploits. Today’s viruses might encrypt all your files and demand a ransom.
Or a hacker might blackmail a large company by threatening to launch a denial-of-service attack, which prevents customers from accessing the company’s website.
More commonly, though, viruses don’t cause any apparent damage or announce their presence at all. Instead, a virus might silently install a keystroke logger, which waits until the victim visits a banking website and then records the user’s account details and password, and forwards them to a hacker via the Internet.
The hacker is an identity thief, using these details to clone credit cards or plunder bank accounts. The victim isn’t even aware that the computer has been infected. Once the virus has done its job,
it may delete itself to avoid detection.
Another trend is for malware to take over your computer, turning it into a remote-controlled zombie. It uses your computer without your knowledge to relay millions of profit-making spam messages. Or, it may launch other malware attacks on unsuspecting computer users.
And as social networks like Facebook and Twitter have grown in popularity, hackers and cybercriminals are exploiting these systems to find new ways of infecting computers and stealing identities.
Hackers may not even target large numbers of victims any more. Such high-visibility attacks bring unwanted attention, and antivirus companies can soon neutralize malware that is widely reported. In addition, large-scale exploits can bring hackers more stolen data than they can handle. Because of this, threats are becoming more carefully focused.
Spearphishing is an example. Originally, phishing involved sending out mass-mail messages that appeared to come from banks, asking customers to re-register confidential details, which could then be stolen. Spearphishing, by contrast, confines itself to a small number of people, usually within an organization. The mail appears to come from colleagues in trusted departments, asking for password information. The principle is the same, but the attack is more likely to succeed because the victim thinks that the message is internal, and his or her guard is down.
Stealthy, small-scale, well-targeted: for now,
this seems to be the way that security threats
are going.
What of the future, though? Predicting how security threats will develop is almost impossible. Some commentators assumed that there would never be more than a few hundred viruses, and Microsoft’s Bill Gates declared that spam would no longer be a problem by 2006. It’s not clear where future threats will come from, or how serious they will be. What is clear is that whenever there is an opportunity for financial gain, hackers and criminals will attempt to access and misuse data.



 by a shift n can be described mathematically as,
by a shift n can be described mathematically as,